Operating principle
Pulsed xenon lamp
A pulsed xenon lamp is basically a quartz tube with electrodes welded on its ends and filled with xenon, a harmless noble gas.

Due to electric discharge of several thousand amperes, the xenon inside the quartz envelope is heated to 10,000-15,000 К. The resulting xenon plasma generates a bright flash of light, in spectral structure similar to the Sun. The lamp generates repeating short (10-4 sec) light flashes with the frequency of several hertz.
Biocidal action
Is based on multichannel impact of continuous spectrum pulsed UV light on all life-critical structures of a bacterial cell, primarily damaging its genetic material (DNA, RNA) and biomembranes. The UV light of continuous spectrum triggers the following destructive processes:
In the DNA molecule
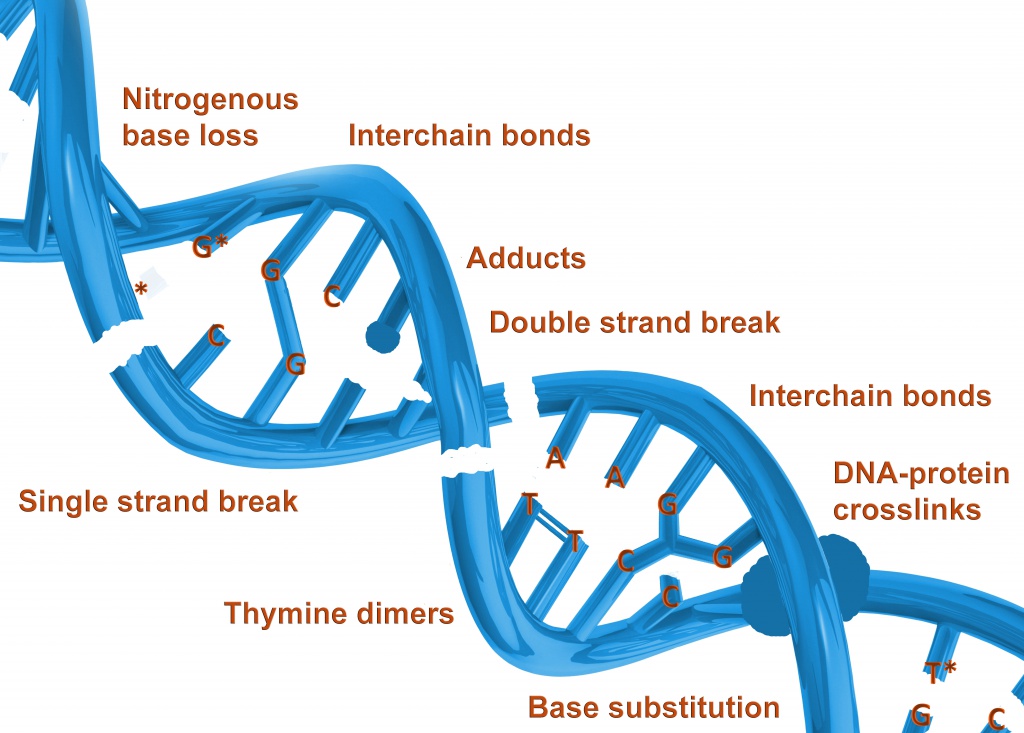
- Formation of thymine dimers under influence of light quanta in the 230-300 nm region, with maximum efficiency at 265 nm;
- Formation of interchain bonds, loss of nitrogen bases (for example, thymine detachment), photolysis of double bonds, single and double strand breaks under influence of light quanta, especially in the 190-300 nm region.
Such multiple (cluster) photochemical damages lead to the DNA molecule destruction.
In biomembranes

Photooxydation of lipids visibly damages the membrane (breaches its integrity causing cytoplasm efflux) which therefore loses its barrier function.
The synergy of the said mechanisms of microorganisms' inactivation (high intensity and photochemical degrading of DNA molecules and cell membrane) by pulsed UV light of continuous spectrum leads to full microorganisms' destruction with high efficiency (99.9-100 %) within shortest time (from 30 seconds).